Anesthesia Techniques
Elevating Care: Anesthesia Support Excellence
Catalysts of Comfort: Navigating Excellence in Anesthesia Support
In the realm of healthcare, the role of anesthesia support is paramount, ensuring that patients undergo medical procedures with safety, comfort, and precision. Anesthesia support professionals, including anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists, play a crucial role in optimizing the patient experience and facilitating successful medical interventions. Let’s explore the multifaceted dimensions of anesthesia support and its pivotal role in healthcare settings.
The Foundation of Patient Safety
Anesthesia support serves as the bedrock of patient safety during medical procedures. Professionals in this field are dedicated to assessing the patient’s medical history, monitoring vital signs, and tailoring anesthesia plans to the individual’s unique needs. The focus on meticulous planning and continuous monitoring contributes to a safe and controlled environment for various surgical and medical interventions.
Tailored Anesthesia Plans for Diverse Procedures
Anesthesia support extends its expertise across a spectrum of medical procedures, ranging from routine surgeries to complex interventions. Professionals collaborate with surgical teams to devise tailored anesthesia plans that align with the specific requirements of each procedure. This personalized approach ensures that patients receive the appropriate type and dosage of anesthesia for their condition and the nature of the intervention.
Pain Management Expertise
Beyond inducing a state of controlled unconsciousness during surgery, anesthesia support is integral to pain management. Professionals work closely with patients to address preoperative anxiety and administer anesthesia that not only ensures unconsciousness but also manages postoperative pain effectively. This dual focus on patient comfort and pain control contributes to a smoother recovery process.
Navigating Anesthesia Techniques
Anesthesia support encompasses a repertoire of techniques, each designed to address different medical scenarios. From general anesthesia, where patients are completely unconscious, to regional anesthesia, which targets specific areas of the body, professionals navigate diverse techniques based on the nature of the procedure and the patient’s medical condition. This versatility allows for flexibility and precision in anesthesia administration.
Continuous Monitoring During Procedures
Throughout medical procedures, anesthesia support professionals maintain vigilant monitoring of vital signs, ensuring the patient’s physiological stability. From heart rate and blood pressure to oxygen saturation levels, continuous assessment allows for prompt interventions if any deviations from the norm occur. This real-time monitoring contributes to the overall safety and well-being of the patient.
Emergency Preparedness and Rapid Response
Anesthesia support professionals undergo extensive training in emergency preparedness and rapid response. While complications during anesthesia are rare, being prepared for any unforeseen circumstances is crucial. Professionals are equipped to handle emergencies swiftly, whether it involves allergic reactions, changes in vital signs, or other unexpected events, ensuring that patient safety remains the top priority.
Collaboration with Surgical Teams
Anesthesia support is a collaborative endeavor that involves close coordination with surgical teams. Effective communication between anesthesiologists, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals is essential for a seamless and successful medical intervention. This collaborative approach ensures that the patient’s overall well-being is prioritized throughout the entire perioperative period.
Postoperative Care and Recovery Support
The responsibilities of anesthesia support extend into the postoperative phase, encompassing care and support
Advanced Anesthesia Techniques: Ensuring Comfort and Safety
Elevating Patient Experience: The World of Advanced Anesthesia Techniques
Anesthesia plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare, ensuring patients undergo medical procedures with comfort and safety. Over the years, advancements in anesthesia techniques have revolutionized the field, contributing to improved patient outcomes and recovery experiences.
Tailoring Anesthesia to Individual Needs
One of the significant strides in anesthesia techniques is the move towards personalized approaches. Anesthesiologists now tailor anesthesia plans to individual patient needs, considering factors such as age, health status, and the specific nature of the medical procedure. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of anesthesia while minimizing potential risks.
Innovative Drug Delivery Systems
Advancements in drug delivery systems have transformed the administration of anesthesia. The development of targeted and controlled-release medications allows for precise dosage management, reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions. These innovative systems contribute to a smoother induction and maintenance of anesthesia, ensuring patients remain comfortable throughout procedures.
Regional Anesthesia: Precision and Reduced Systemic Impact
Regional anesthesia techniques have gained prominence for their precision and ability to minimize the systemic impact of anesthesia. Procedures such as epidurals and nerve blocks target specific regions of the body, providing pain relief without affecting the entire nervous system. This approach is particularly beneficial for certain surgeries and chronic pain management.
Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA): Enhanced Control and Rapid Recovery
Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA) represents a significant advancement in anesthesia administration. Unlike traditional methods that involve inhalation agents, TIVA relies solely on intravenous medications. This technique offers enhanced control over anesthesia levels, leading to smoother recovery and reduced postoperative side effects. TIVA has become a preferred choice for various surgical procedures.
Depth of Anesthesia Monitoring: Ensuring Optimal Sedation
Monitoring the depth of anesthesia is a critical aspect of ensuring patient safety. Technological innovations now allow for real-time tracking of a patient’s sedation level, enabling anesthesiologists to make immediate adjustments as needed. This precision in monitoring contributes to a more controlled and stable anesthesia experience.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS): Integrating Anesthesia into a Holistic Approach
Advanced anesthesia techniques play a vital role in the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocol. By integrating anesthesia into a comprehensive approach that includes preoperative optimization and postoperative care, patients experience faster recoveries with reduced pain and complications. ERAS represents a paradigm shift towards a patient-centered, multidisciplinary model of care.
Pediatric Anesthesia: Safeguarding the Well-being of Young Patients
Anesthesia techniques for pediatric patients require specialized considerations. Innovations in pediatric anesthesia focus on minimizing stress, ensuring pain control, and tailoring dosage based on age and size. Child-friendly approaches, such as the use of flavored masks and engaging preoperative preparations, contribute to a positive experience for young patients.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Distraction Techniques
Addressing the psychological aspect of anesthesia, virtual reality (VR) and distraction techniques have gained recognition. These methods help alleviate preoperative anxiety and discomfort by immersing patients in calming virtual environments. Integrating technology in this way enhances the overall patient experience and contributes to a more positive perception of anesthesia.
To explore the world of
Mastering Anesthesia Techniques: Ensuring Comfort and Safety
![]()
Mastering Anesthesia Techniques: Ensuring Comfort and Safety
Anesthesia techniques are integral to modern medical procedures, ensuring patients experience comfort and safety during surgery or other interventions. This article delves into the diverse realm of anesthesia techniques, highlighting their significance in the healthcare landscape.
The Art and Science of Anesthesia
Anesthesia is both an art and a science. Anesthesia techniques involve the administration of drugs to induce a state of controlled unconsciousness, pain relief, and muscle relaxation. Anesthesiologists, the specialists in this field, meticulously tailor their approach to each patient and procedure, considering factors such as the patient’s medical history, the type of surgery, and the desired depth of anesthesia.
General Anesthesia: Inducing Controlled Unconsciousness
General anesthesia is perhaps the most well-known form of anesthesia. It involves administering medications to induce a state of unconsciousness, allowing patients to remain completely unaware and pain-free during surgical procedures. Anesthesiologists closely monitor vital signs and adjust the anesthesia depth throughout the surgery to ensure the patient’s safety and comfort.
Regional Anesthesia: Targeted Pain Relief
Regional anesthesia targets specific regions of the body, providing pain relief while the patient remains conscious. Techniques like epidurals and spinal blocks are common in procedures such as childbirth or certain orthopedic surgeries. Regional anesthesia offers the advantage of localized pain control, minimizing the need for general anesthesia and reducing postoperative discomfort.
Local Anesthesia: Precision in Pain Management
Local anesthesia is employed for minor procedures or to numb a specific area of the body. This technique involves injecting anesthetic agents directly into the target area, temporarily blocking sensation. Local anesthesia is commonly used in dermatological procedures, dental work, or minor surgeries, ensuring precision in pain management without affecting the patient’s overall consciousness.
Balancing Depth of Anesthesia: The Role of Monitoring
Achieving the right depth of anesthesia is critical for patient safety. Continuous monitoring of vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, is an integral part of anesthesia techniques. Modern monitoring technology allows anesthesiologists to make real-time adjustments, ensuring the patient’s physiological parameters remain within safe ranges throughout the procedure.
Emerging Technologies in Anesthesia
Advancements in technology continue to shape anesthesia techniques. From sophisticated monitoring devices to the integration of artificial intelligence, these innovations enhance the precision and safety of administering anesthesia. Anesthesiologists leverage these technologies to tailor their approaches, taking into account individual patient responses and optimizing outcomes.
Pediatric Anesthesia: Special Considerations for Young Patients
Administering anesthesia to pediatric patients requires specialized expertise. Pediatric anesthesia techniques consider the unique physiological and developmental characteristics of children. Anesthesiologists carefully calculate drug dosages, monitor vital signs, and create an environment that ensures the safety and well-being of the young patient throughout the procedure.
Anesthesia in Ambulatory Settings: Maximizing Efficiency
The evolution of anesthesia techniques has facilitated their application in ambulatory or outpatient settings. Ambulatory anesthesia focuses on minimizing the duration of sedation, allowing patients to recover quickly and return home on the same day. This approach maximizes efficiency while maintaining the highest standards of safety and comfort.
Patient Education and
Innovative Anesthesia Techniques for Safer Surgeries and Recovery

Exploring Modern Anesthesia Techniques for Enhanced Patient Care
Anesthesia plays a crucial role in modern medicine, ensuring that patients undergo surgical procedures with minimal discomfort and risks. Advancements in anesthesia techniques have not only improved the safety of surgeries but also contributed to more efficient recovery processes. Let’s delve into the innovative approaches shaping the landscape of anesthesia.
Precision in Dosage and Administration
One of the significant advancements in anesthesia is the precision achieved in dosage administration. Anesthesiologists now have access to sophisticated monitoring tools and precise delivery systems, allowing them to tailor the dosage to each patient’s unique needs. This precision enhances the safety of anesthesia, reducing the risk of complications during and after surgery.
Regional Anesthesia: Targeting Specific Areas for Pain Relief
Regional anesthesia techniques have gained prominence for their ability to provide targeted pain relief to specific regions of the body. This approach minimizes the need for general anesthesia, reducing the overall impact on the patient’s body. Techniques like epidurals and nerve blocks are commonly employed, not only for surgical procedures but also for postoperative pain management.
Innovative Approaches to General Anesthesia
General anesthesia remains a cornerstone in various surgical interventions, and recent innovations have focused on refining this approach. From advanced inhalation agents to intravenous drugs with rapid onset and offset, these innovations aim to achieve a more controlled and predictable anesthesia experience. Anesthesia providers continuously explore ways to optimize patient safety and comfort.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Protocols
Anesthesia is not only about inducing unconsciousness; it is also a key player in the evolving field of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS). Collaborating with surgeons and other healthcare professionals, anesthesiologists contribute to the development and implementation of ERAS protocols. These protocols focus on minimizing stress, optimizing nutrition, and promoting early mobility for faster recovery.
Technology Integration for Monitoring and Control
The integration of technology in anesthesia goes beyond precise dosage delivery. Monitoring systems now provide real-time data on vital signs, allowing anesthesiologists to promptly respond to any deviations. Additionally, automated systems assist in the control of anesthesia levels, ensuring a delicate balance between maintaining unconsciousness and minimizing potential side effects.
Pediatric Anesthesia: Ensuring Safety for Young Patients
Anesthesia for pediatric patients requires specialized considerations, and techniques have evolved to address the unique needs of children. From age-appropriate dosage calculations to child-friendly induction methods, pediatric anesthesia aims to provide a safe and comfortable experience for the youngest surgical patients.
Balancing Analgesia and Avoiding Opioids
In the midst of the opioid crisis, anesthesia techniques are adapting to minimize the reliance on opioids for pain management. Multimodal analgesia approaches, combining different medications and interventions, are becoming more prevalent. This shift not only helps in controlling pain effectively but also contributes to reducing the risk of opioid-related complications.
Patient-Centered Care and Informed Decision-Making
Modern anesthesia practices emphasize patient-centered care and informed decision-making. Anesthesiologists engage in thorough preoperative discussions with patients, explaining the anesthesia plan, potential risks, and expected outcomes. This collaborative approach ensures that patients are active participants in
Navigating Anesthesia: Advanced Techniques
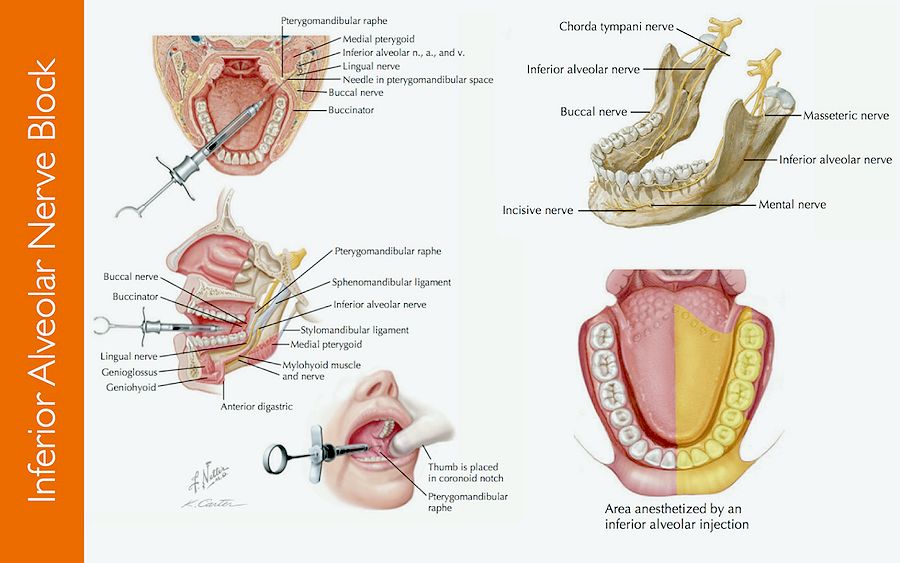
Navigating Anesthesia: Advanced Techniques
Anesthesia is a critical component of many medical procedures, ensuring patient comfort and safety. Advancements in anesthesia techniques have revolutionized the field, providing healthcare professionals with a range of options to tailor anesthesia to individual needs. Let’s explore the landscape of anesthesia techniques and their transformative impact on modern healthcare.
Evolution of Anesthesia Techniques
The evolution of anesthesia techniques has been marked by milestones, from the early use of ether and chloroform to the development of modern inhalation and intravenous anesthetics. Technological innovations and a deeper understanding of pharmacology have contributed to the refinement of anesthesia administration, enhancing both efficacy and safety.
Inhalation Anesthetics: Balancing Depth and Precision
Inhalation anesthetics remain a cornerstone of anesthesia techniques. These agents are administered through inhalation, allowing for precise control over the depth of anesthesia. Advancements in inhalation anesthetics include the use of sevoflurane and desflurane, which offer rapid onset and offset of anesthesia, minimizing recovery times for patients.
Intravenous Anesthesia: Swift and Targeted Effects
Intravenous (IV) anesthesia has gained prominence for its swift and targeted effects. Propofol and etomidate are examples of intravenous anesthetics that induce anesthesia rapidly. The ability to titrate IV anesthetics allows anesthesiologists to maintain a specific level of sedation, ensuring patient comfort during various medical procedures.
Regional Anesthesia: Precision and Limited Sensation
Regional anesthesia involves numbing a specific part of the body, providing both pain relief and preserving consciousness. Techniques like epidural and spinal anesthesia are commonly used for surgeries involving the lower abdomen, pelvis, or lower extremities. Regional anesthesia offers the advantage of targeted pain control with reduced systemic effects.
Peripheral Nerve Blocks: Localized Pain Management
Peripheral nerve blocks are a subset of regional anesthesia that involves injecting anesthetic agents near peripheral nerves. This technique is particularly useful for extremity surgeries, providing localized pain management while allowing patients to remain awake and aware during the procedure. Peripheral nerve blocks contribute to enhanced postoperative pain control.
Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC): Tailored Sedation
Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) involves providing sedation while continuously monitoring vital signs. This technique is commonly used for less invasive procedures, allowing patients to be in a state of conscious sedation. MAC offers the advantage of tailoring sedation levels based on the procedure’s complexity and the patient’s comfort.
Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA): Precise Control
Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA) involves administering all anesthetic agents intravenously without the use of inhaled agents. TIVA provides precise control over anesthesia depth and is often preferred for certain surgeries, including those requiring controlled hypotension. The avoidance of inhalation agents may be beneficial for patients with specific respiratory considerations.
Ultrasound-Guided Anesthesia: Enhanced Precision
Advancements in technology have introduced ultrasound-guided anesthesia, enhancing precision in nerve blocks and other regional anesthesia procedures. Ultrasound allows real-time visualization of anatomical structures, enabling anesthesiologists to target nerves more accurately and reduce the risk of complications.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS): Integrating Anesthesia Techniques
Anesthesia techniques play a vital role in the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) approach. ERAS focuses on optimizing preoperative, intraoperative, and